Active-active high availability clusters distribute workloads evenly across all nodes, ensuring optimal load balancing. In contrast, an active-passive setup keeps nodes on standby, activating them only when the primary fails, leading to potential delays. Active-active configurations offer reduced downtime and improved performance, making them the preferred choice for continuous system availability.
Many organizations that can’t afford unexpected downtimes use high availability (HA) clusters to keep mission-critical business processes running smoothly. HA clusters typically come in two types: active-active and active-passive. While both HA clusters can provide a high level of resiliency, they’re designed for different use cases.
In this blog post, you’ll learn how to differentiate these two types of high availability cluster configurations and determine which one to employ in a given scenario.
Active-active high availability cluster
An active-active configuration consists of two or more active nodes that provide similar services to multiple clients or requesting parties at the same time. For example, in a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) active-active cluster, all active servers provide SFTP services to SFTP clients. This configuration improves fault tolerance and reduces downtime since the total traffic and workload is shared across all participating nodes instead of being handled by a single node.
Since traffic is shared, each node can run at a lower capacity, avoid the risk of overload and achieve better performance. With each node capable of processing requests at a faster rate, overall traffic throughput can remain high. This can only be beneficial to end users. Your users should experience better response times and minimal, if not zero, interruptions.
Active-active clusters are scalable. In fact, the more nodes you add to the cluster, the more effective it can be at improving throughput and user experience while reducing the risk of downtime.
This scalability makes active-active HA clusters ideal for businesses that need to support high traffic volumes or a rapidly growing user base.
- While businesses often use SFTP for data transfer and file-sharing, SFTP servers lack automation, high availability, and system integration capabilities.
- A managed file transfer (MFT) solution like JSCAPE MFT by Redwood not only supports SFTP and other protocols (FTP/S, HTTP/S, AS2, OFTP) but also includes built-in automation, high availability, and integration functionality, making it ideal for comprehensive B2B file transfer workflows.
- Other MFT solutions may only offer active-passive high availability, with no backup server actively running in real-time for disaster recovery
- If and when an issue is detected, the stand-by/passive servers must first start-up and then take over, building in lag. Ready to ditch the SFTP server to see how much more reliable your automation and file transfers can be? Experience JSCAPE’s active-active architecture.
- Get a free trial when you request it here

Role of a load balancer in an active-active HA cluster
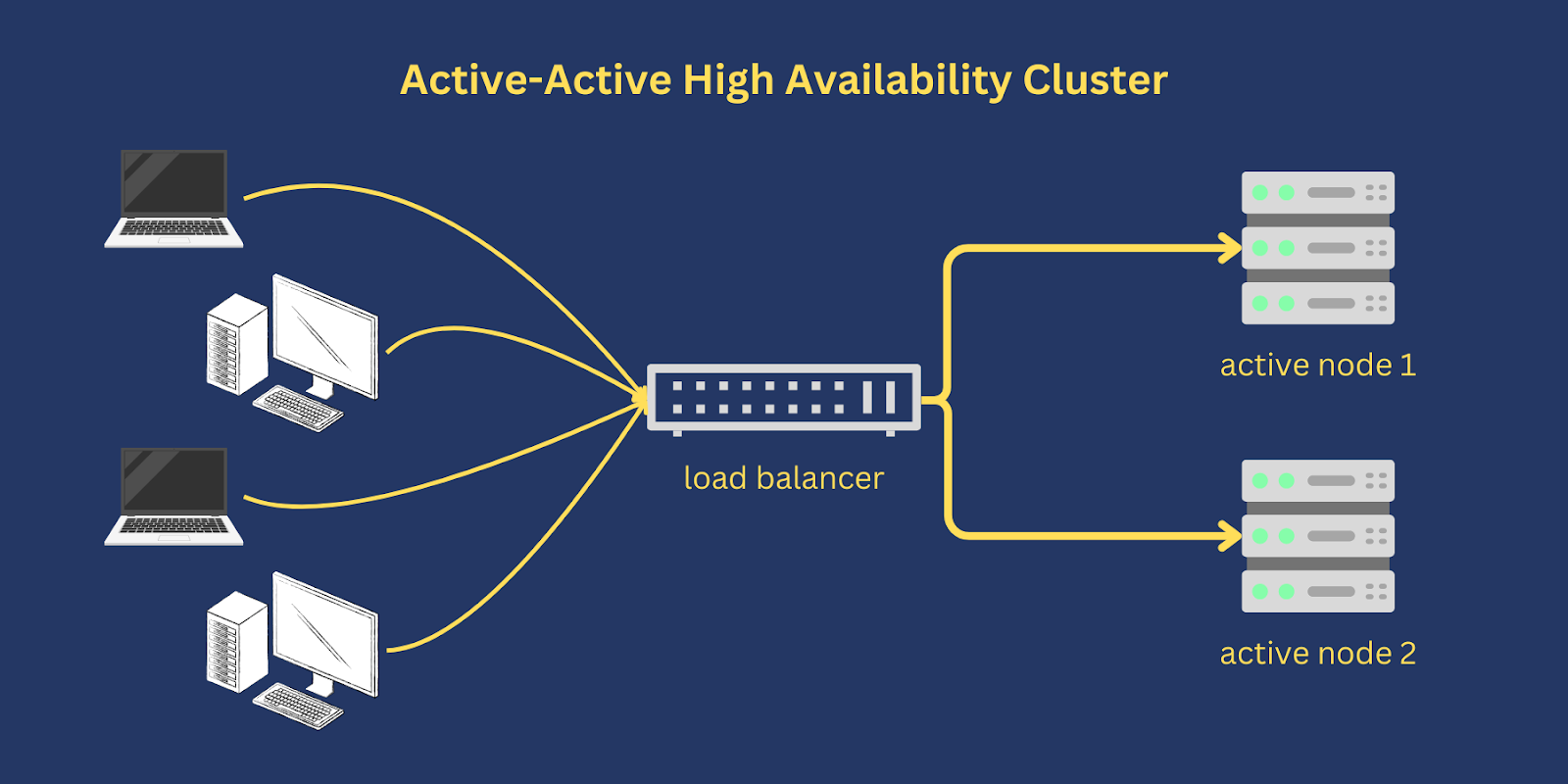
Many active-active clusters rely on a dedicated load balancer for routing or distributing traffic across all participating nodes. The manner by which a load balancer distributes traffic depends on the specific load balancing algorithm used. For instance, some load balancers distribute traffic using Round-Robin, Weighted Round Robin or Random algorithm.
Some load balancers, like JSCAPE MFT Gateway by Redwood, support multiple load balancing algorithms. This gives you flexibility in choosing the most suitable load balancing method for your organization. Should you wish to learn more about different load balancing algorithms, you may read our blog post “Comparing Load Balancing Algorithms.”
Certain load balancers also have a way of monitoring the health of your HA cluster. JSCAPE MFT Gateway, for instance, can detect if a node fails and will temporarily remove that node from the cluster. Not only that, it can send notifications to a designated server administrator so that the admin can take appropriate action.
Active-passive high availability cluster
Like the active-active configuration, an active-passive configuration also consists of two or more nodes. The key difference is that, unlike active-active wherein all participating nodes are active at the same time, only one node is active in an active-passive HA cluster at any given time. All other nodes act as backups that can readily take over if the active or primary node fails.
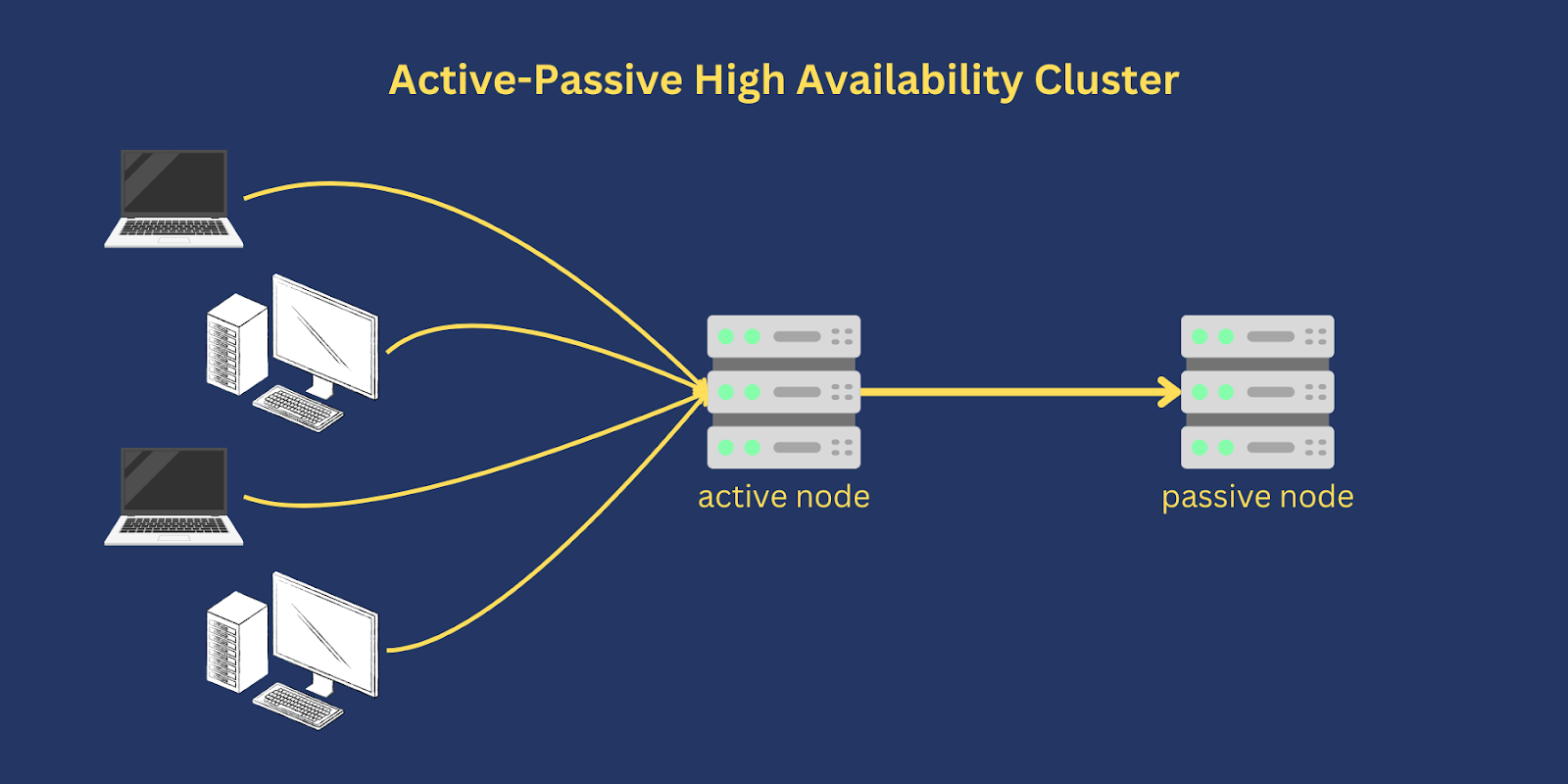
Active-passive setups are common in disaster recovery (DR) strategies. In some DR strategies, the passive node is set up in a separate geographical location and then brought into play once the active node becomes incapacitated. You can, for example, deploy your primary node in your on-premise data center and your failover node in a cloud environment like Amazon Web Service (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
The role of redundancy in HA clusters
Regardless of the type of HA cluster you use, it’s usually important to ensure redundancy among all participating nodes in your cluster. This means, as much as possible, each node must be a replica of every other node in the cluster.
In high availability file transfer systems, for instance, it’s important for all nodes to have the same properties and configurations. That way, when a user logs in to any node, the user will be able to connect to the same set of services and see the same files, folders and user interface.

Which HA cluster should you use?
Let’s now talk about the specific use cases that each HA cluster is best suited for.
If you need to support high traffic volume: Active-active
Assuming all nodes are redundant and, hence, have equal capacity, the active node of an active-passive HA cluster can reach maximum capacity faster than the nodes of an active-active HA cluster. That node can reach maximum capacity even faster if the cluster is subjected to high traffic volume. Of course, that’s not a good thing. If you need to support high traffic volume, you’d want a cluster that won’t be easily overwhelmed. Thus, an active-active cluster would be more suited for this use case. Want to see it in action? Get a Demo to see for yourself.

If you need to provide a good user experience: Choose active-active
Since the active node of an active-passive cluster has to handle all client requests, an active-passive cluster won’t be able to provide the same level of throughput and response time as an active-active HA cluster. If your goal is to provide an optimal user experience, deploy an active-active cluster.
Achieve any high availability file transfer configuration with JSCAPE MFT
If you’re looking for a file transfer solution with high availability capabilities, we invite you to try JSCAPE MFT by Redwood. JSCAPE MFT supports all major file transfer protocols and can run on all major operating systems. Not only that, it also comes with a cloud-based option delivered under a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, JSCAPE MFTaaS. JSCAPE MFT supports both active-active and active-passive HA configurations, giving you maximum flexibility in choosing the best HA configuration for your organization.
Get Your Free Trial
The next step is for you to try JSCAPE MFT Server for yourself. JSCAPE is platform-agnostic and can be installed on Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, and Solaris. It can handle any file transfer protocol and multiple protocols from a single server. Additionally, JSCAPE enables you to handle any file type, including batch files and XML.
Get a free trial of JSCAPE MFT Server when you request it here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an active-active high availability cluster?
An active-active high availability cluster is one of the two most frequently used high availability (HA) cluster configurations. They normally consist of a minimum of two nodes that are running identical services or workloads at the same time. An active-active high availability cluster distributes workloads evenly across a set of nodes to provide load balancing. This way, no single node will get overloaded, and response times are improved. Different types of load balancing algorithms, such as “round robin,” can be used to assign clients to active nodes.
What is an active-passive high availability cluster?
The second of the two most frequently used high availability (HA) cluster configurations is the active-passive cluster. In this configuration, not all nodes are active. For example, if there are two nodes in an active-passive cluster, one would be active and running a service or other workload. The second node would be identical to the first node, but in standby, ready to take over if the active node encounters an issue. All clients are served by active nodes in an active-passive cluster, while no clients are sent to the passive, failover nodes unless there is a problem with an active one.
What are the types of high availability clustering?
High availability clusters are groups of nodes with identical, redundant configurations that are used to provide continuous availability. High availability clusters are generally used for load balancing, backup, and failover purposes. The two most commonly used types of high availability clusters are active-active (all nodes are active and receive clients), and active-passive (some nodes are active, and other nodes are passive, serving as failovers).
Learn how to simplify high availability clustering through datastores





