If you need to clear some space on your file transfer protocol (FTP) server, you can leverage JSCAPE by Redwood triggers to automatically delete old files. Check out our illustrated tutorial.
The benefits of deleting old files
Organizations can take advantage of JSCAPE triggers to automate activities on their SFTP, FTPS or FTP server. One unique benefit of JSCAPE triggers, especially for large organizations, is the ability to monitor certain directories for aging files. Deleting old files not only improves performance by freeing up resources, but it also strengthens an organization’s security posture by eliminating the risk of exploitation through an older unsecured file. In this tutorial, we’re going to show you how to use triggers and any supported protocol to automatically delete old files in JSCAPE MFT Server by Redwood.
What is an FTP server, and why does file deletion matter?
An FTP server is a specialized software application that facilitates the transfer of files between an FTP client (user) and a server over a network. It uses the file transfer protocol to allow FTP users to upload, download and manage files on the server, much like accessing files stored locally.
Common use cases
However, your files can get backed up and cluttered over time if you’re not properly managing them. Part of managing your organization’s file transfer system is knowing when to delete files that are old, temporary or no longer relevant. Consistently deleting files using an FTP server will help your organization stay compliant, reduce cybersecurity risks, clear up storage space and improve its system performance.
Some ways you can use an FTP server to attain these benefits include:
- Clearing storage and improving performance: Deleting old files, especially temporary and unnecessary ones, can lead to faster boot times, quicker program launches and smoother overall operations because your device will have less data to sift through when searching for files or loading applications.
- Compliance purposes: Many compliance mandates require data to be retained and disposed of properly, and deleting old files adheres to these policies.
- Reducing risk: By eliminating old files from the server entirely, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access or exploitation through the dated files.
Trying to manually delete files using syntax can be difficult as your organization scales its operations. However, maintaining a file deletion process is easy when you use an FTP server and an MFT solution that has automation capabilities like JSCAPE.
Automating file deletion with JSCAPE MFT Server
Automation makes file deletion easy and consistent without manual labor. For example, you can follow this automated file transfer tutorial to automatically delete files once they’re a year old. Every night, at 9:30 PM, JSCAPE MFT server should scan the contents of a particular directory and look for files that have this minimum age. You can specify any age, but this example will use 365 days or 1 year. If any such files are found, the server should then automatically delete those files.
So, for example, if today is March 4, 2015, these three files would be deleted.

To achieve this, you’ll need:
- A directory monitor that will scan a specific directory for one-year-old files
- A trigger that will activate the directory monitor every night at 9:30 PM; and
- Another trigger that will automatically delete each one-year-old file found by the directory monitor
Now that you have a plan, here are the steps on how you can put that plan into action.
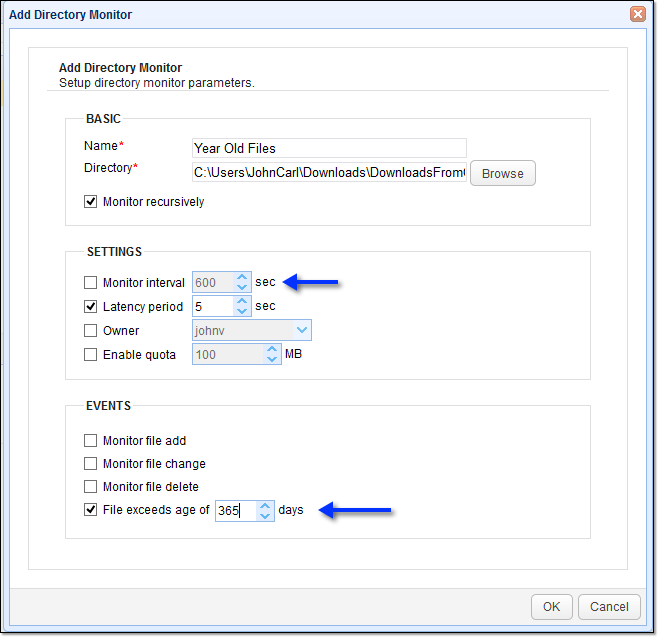
Create a directory monitor to detect old files
- Go to the Directory Monitor node to create a new one
- Name the monitor
- Select the Browse button
- Choose the directory that contains the files you want to monitor
- Uncheck the Monitor interval checkbox
- Go to the EVENTS panel and check the File exceeds age of box
- Type in the number of days in which you want your file deletion to begin. For example, if you want to delete one-year-old files, enter 365
- Select the OK button
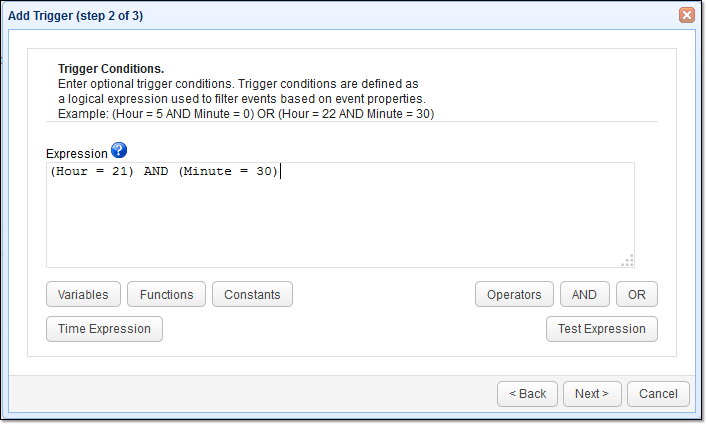
Once you’ve created the directory monitor for detecting old files, the next step is to create a trigger that will activate that directory monitor every night at 9:30 PM.
Create a trigger that would activate the directory monitor every night
- Go to the Triggers node to add a new one
- Name the trigger
- Select Current Time from the Event type drop-down list
- Select the Next button
- Specify the time at which this trigger should execute; then click Next
- Expand the drop-down list box and select the Run Directory Monitor trigger action
- Select the name of the directory monitor you created earlier
- Click the OK button
You are now ready to proceed to the last step.

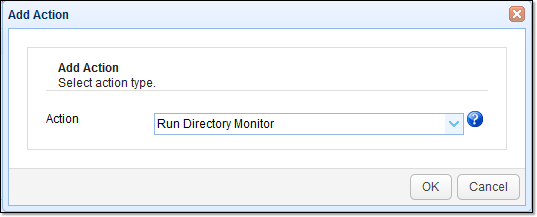

Create a trigger that would run each time an aged file is detected and then subsequently delete that particular file.
Add another trigger and give it an appropriate name (e.g. “Nightly File Deletes”). Expand the Event type drop down list and select Directory Monitor File Aged. Click Next to continue.
- Add and name another trigger
- Choose the Directory Monitor File Aged option from the Event type drop-down list
- Enter the following text into the Expression box: Monitorname = “What you named your monitor in the first part of this process”
- Select the Delete File option from the Action drop-down list
- Select OK
That’s it. Now you know how to automatically delete old files from your MFT server.




Best practices for file deletion
Deleting files from your organization’s system requires care and control because you don’t want to prematurely or incorrectly delete data. Always verify the full file path before you delete a file to ensure the correct one is targeted and avoid removing critical data. Use detailed logging to track deletion events for auditing and recovery purposes. Implement role-based permissions so that only users who pass authentication tests can remove files to reduce the risk of mistakes or misuse. If a file is deleted using scripts or automation, test those scripts in a non-production environment first to catch errors before they impact live systems.
Troubleshooting errors
If your automated file deletion process fails, it might be due to one or more common issues. Some common errors and their resolutions include:
- File in use: This occurs when another process is locking the file. It can often be resolved by retrying the operation after a short delay or ensuring the file is not open elsewhere.
- Incorrect path: This may result from typos or outdated file references, so double-check the full path before executing deletion.
- Permission denied: This usually indicates that the user or script lacks sufficient rights to delete the file. In this case, confirm that the correct user access controls are in place and that the deletion is allowed under the current role-based settings.
For FTP transfers, passive and active mode settings can also cause unexpected behavior. Find out which modes your client and server support to help resolve connectivity-related errors during your organization’s file operations.
Gain better control with automated file transfer workflows
Find out how JSCAPE makes file management and file transfer much easier for enterprise organizations that value security and efficiency. With built-in automation capabilities, JSCAPE lets you schedule, monitor and manage file transfers without manual intervention. This helps your organization reduce the risk of human errors and saves valuable time across IT operations.
Download JSCAPE MFT Server Trial
Recommended reads
You might also find these posts interesting:





