The days of HTTP pages on the Web appear to be numbered. Google has announced it would be labelling certain HTTP pages as “Not secure” when it releases Chrome 56 on January 2017. This is part of Google’s ongoing effort to increase adoption of HTTPS. HTTPS is reinforced by SSL/TLS, making it a more secure version of HTTP
HTTPS primarily provides data-in-motion encryption, which protects transmitted data from man-in-the-middle attacks. In HTTP, data is transmitted in plaintext. This makes it vulnerable to eavesdroppers who might want to acquire sensitive information from the HTTP transmission.
In addition to its encryption capabilities, HTTPS also comes with digital certificates, which enable authentication as well as data integrity and non-repudiation. These security elements (i.e. encryption, authentication, data integrity, non-repudation) are crucial to business transactions and other sensitive web activities that require secure communications. That’s why Google is initially targeting websites that transmit passwords or credit card information.
In the current version, Chrome 53, the address bar of a typical login page looks like this:
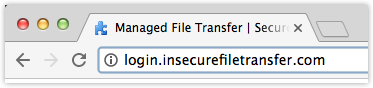
But when Chrome 56 rolls out, that same address bar will display something similar to this:
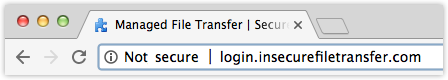
Yet, Google doesn’t intend to stop there. Eventually, Google will be labelling all HTTP web pages (not just pages that accept passwords and credit card data) “Not secure” and will even change the text to red as well as replace the exclamation mark icon with a red warning triangle icon that’s currently associated with broken HTTPS.
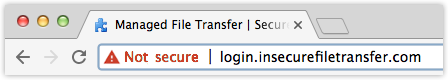
The intention is to make it unmistakably clear to users that the HTTP site they’re visiting or transacting with is insecure. This will hopefully make them think twice before proceeding.
For those who are still on the fence regarding HTTPS adoption, you might want to know that 1) an HTTPS page could get a boost in search rankings and 2) HTTPS is more affordable than ever before.
This announcement was posted on the Google Security Blog.
Related posts
What HSTS Is and How It Enhances The Effectiveness of HTTPS
How to Set Up a Web File Transfer
Setting Up A HTTPS To HTTP Reverse Proxy
SSL vs TLS – Know The Difference





