How to secure and protect data at rest

To prevent confidential data from leaking out of your organization or getting stolen, your cyber security efforts have to be aimed at two areas: securing data-at-rest and securing data-in-transit (sometimes referred to as data-in-use). Data-in-transit is often secured by protocols that use an Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and require encryption keys. But what about data-at-rest protection?
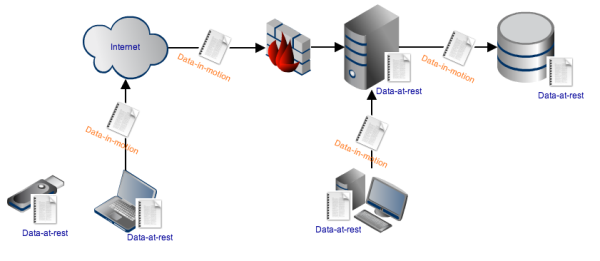
What Is Data At Rest?
Data-at-rest refers to data in storage devices such as on-site and offsite backup tapes or servers in a storage area network (SAN), plus file systems and any other data that isn’t being transmitted through a network (which is then known as data-in-transit/motion).
Protecting Data Under Threat
A lot of the data being stored in IT systems and devices these days contain sensitive information. This can range from trade secrets and financial data to personal information. These types of information can be highly valuable to competitors and cyber criminals. Competitors can use certain kinds of information to gain an unfair advantage, while cyber criminals can sell certain types of data on the dark web or in other shady marketplaces.
But why target data at rest? Well, compared to data-in-motion, which is data that's in transit on a network, data at rest is easier to acquire. If the data is stored in a portable device like a USB stick, a mobile device or a laptop, the attacker can simply steal that device. They can even steal an entire hard drive.
Even if the data isn't in a portable device, the prospect of getting hold of a large volume of valuable information from just one place (like a database or a server) is enough motivation to break into systems storing data-at-rest.
Compliance Standards Impacting Data At Rest
The growing number of data breach incidents and the ensuing cases of identity theft have prompted legislators to create laws designed for protecting personally identifiable information (PII). Many of these laws impact the way you currently deal with data at rest. That is, if you want to avoid onerous obligations and costly penalties, you will have to adopt better ways of securing PII taking the form of data at rest.
Some of the most prominent laws and regulations that are impacting IT systems are HIPAA, GLBA, PCI DSS and GDPR.
HIPAA-HITECH
With maximum penalties of up to $1.5 million per year and possible imprisonment, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, which is an amended version of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a significant and important piece of legislation from both an IT and administrative standpoint in the health care industry.
Aimed at preventing unauthorized disclosures of electronic protected health information (ePHI), HIPAA-HITECH is directing medical practitioners, health care providers, hospitals, and their business associates to review information security in their EHRs (Electronic Health Records) and similar IT systems.
GLBA
While HIPAA-HITECH deals with ePHI, which is basically PII found with medical information, the GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act), on the other hand, focuses on nonpublic personal information or NPI. This is just the name given to PII found alongside financial information, examples of which include: SSNs, people’s names, addresses, phone numbers, bank account numbers, credit card numbers, as well as income and credit histories.
Such information is commonly stored in a financial institution’s database. If someone gains unauthorized access to that database, and ePHI ends up in the wrong hands, the financial institution in question could end up paying $100,000 per violation, while its officers and directors can be fined with up to $10,000 per violation.
PCI DSS
The PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards) is a set of standards aimed at securing cardholder data, such as the Card Security Code (CSC), cardholder's name, expiration date and (most importantly) the Primary Account Number (PAN), among others. Several organizations that deal with cardholder data, including merchants, processors, acquirers, issuers and service providers are all subjected to the data protection requirements of PCI DSS.
In order to meet the requirements, these organizations have to implement a laundry list of security measures on various system components where cardholder data is transmitted, processed, or stored. There are 12 requirements all in all and at least one (Requirement #3 Protect stored cardholder data) specifically caters to securing data-at-rest.
GDPR
Across the pond, the most restrictive data protection law there and perhaps (owing to the fact that the EU is more sensitive about data privacy compared to the US) practically anywhere on the planet is the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Although crafted by the European Union, the GDPR impacts any company which collects data of EU citizens and residents.
Other laws and regulations that call for better protection of data at rest include SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) and U.S. state/territorial data breach notification laws.
How To Implement Data-At-Rest Encryption
With so many regulations to look out for, the need to seek out better ways to secure data is more pressing than ever. You can start by implementing good practices, particularly when dealing with sensitive information. This can include an audit of policies and processes to identify risks of data loss and unauthorized access.
You can also reduce the amount of sensitive data that you collect from employees and customers. Sensitive data that isn't business critical should be discarded in a secure fashion. The objective of both exercises is to reduce the exposure to risk.
Any sensitive data that really must be retained needs to be identified and located. Knowing "what they are" will help you pinpoint which laws and regulations you are answerable to (e.g. ePHI = HIPAA, cardholder data = PCI DSS, although there are usually overlaps). On the other hand, knowing ‘where they are’ will help you carry out your data protection initiatives more effectively and efficiently.
Once you’ve identified what data needs protection and where you can find it, you can then implement various data protection schemes using encryption solutions, authentication mechanisms, disk encryption, access control and so on.
Want some concrete examples on how to secure and protect data-at-rest? We've got several posts and tutorials about the subject. Check out these articles about about data-at-rest security using encryption.
Get A Free 7-Day Trial
Does your business operations involve a lot of sensitive data? If so, it's your duty to make sure that data stays secure for its entire lifecycle, both in transit and at rest. JSCAPE MFT Server, a managed file transfer server, is platform agnostic and enables users to handle multiple protocols from a single server. This helps streamline key management and the security of data behind your firewalls by allowing you to manage all your file transfers from a single pane of glass.
JSCAPE users can also encrypt data-at-rest with OpenPGP cryptography, so that sensitive files are unreadable until a partner decrypts the files at their own endpoint.
Get Your Free Trial
Would you like to try this yourself? JSCAPE MFT Server is platform-agnostic and can be installed on Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS X and Solaris, and can handle any file transfer protocol as well as multiple protocols from a single server. Additionally, JSCAPE enables you to handle any file type, including batch files and XML. Download your free 7-day trial of JSCAPE MFT Server now.
Download JSCAPE MFT Server TrialRelated Content
How To Protect FTP Passwords From Brute Force Attacks
Forward Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy Servers